အာန္တိဗိသြတိစ်
အာန္တိဗိသြတိစ် (ဝါ) ပဋိဇဳဝ (antibiotic) ဂှ် ဒှ်ဂြန်ဓါတု မလၞိန်ဗပိန် ဇဳဝသၟတ် ဗီုကဵု စၟဗက်တေရဳယျာ၊ ပတိုဟ် ကေုာံ ပရဝ်တဝ်ဇြဝ် (protozoa)တအ်ရ။ ဂဥုဲအာန္တိဗိသြတိစ် (ဝါ) ဂဥုဲပဋိဇဳဝဂှ် စကာဒၟံင် ဗွဲမလှဲလး သွက်ဂွံလွဳ ကေုာံ စဵုဒၞာ ယဲသရ (ဝါ) ယဲမဒးစၟဂမၠိုင်[၁][၂] ဂဥုဲဂှ် ဍေဟ် ဂစိုတ် ဗက်တေရဳယျာ ဟွံသေင်မ္ဂး ပဒေါအ်လဝ် ညံင်ဗက်တေရဳယျာ ဟွံဂွံဗြေဝ်တိုန်ရ။ ဂြန်ဓါတုအာန္တိဗိသြတိစ်လ္ၚဵုတအ်ဂှ် ဖန်ဗဒှ်ကၠောန်လဝ် အာန္တိပရဝ်တဝ်ဇြဝ် မဒှ်ဂဥုဲမဂစိုတ် ပရဝ်တဝ်ဇြဝ် မဒှ် ဇဳဝမွဲကလာပ်ရုပ်ကီုရ။[၃] အာန္တိဗိသြတိစ်ဂှ် ဍေဟ်ဟွံလၞိန်ဗပိန် ဝဳရုသ်ဂမၠိုင် (viruses) ဗီုကဵု ဇွဟ်ချာမ်တအ်[၄] ဂဥုဲမလၞိန်ဗပိန် ဝဳရုသ်တအ်ဂှ် ညးကော်စ ဂဥုဲအာန္တိဝဳရုသ်။
ဝေါဟာရမ္ဂး အာန္တိဗိသြတိစ် (antibiotic)— ကၠာဲအဓိပ္ပါယ် အတိုင်အက္ခရမ္ဂး "ဒစဵုဒစး လမျီု"၊ မကၠုင် နူ အရေဝ်ဂရိတ် ἀντι anti (အာန္တိ), "ဒစဵုဒစး" ကဵု βίος bios (ဗိသြသ်), "လမျီု"— ကီုလေဝ် ဝေါဟာရဝွံ ရန်တၟအ် မလၞိန်ဗပိန် စၟမဍောတ်သောဲ မဳခရဝ်ဗေသ်တအ်တုဲ၊ ပ္ဍဲကဵုဝေါဟာရ ဂဥုဲမ္ဂး အာန္တိဗိသြတိစ် antibiotics ဗီုကဵု ပေန်နိသဳလ်လိန် (penicillin) ဂှ် ဒှ်အရာမပ္တိတ် နူကဵု သဘာဝ သတ်မဳခရဝ် (microorganism) မဂွံဆဵုကေတ် နူပတိုဟ် မဗတိုက်သရိုဟ် သတ်မဳခရဝ်တၞဟ်တအ်ရ။ အာန္တိဗိသြတိစ် မကၠောန်ပ္တိတ် နကဵုဂြန်ဓါတု (ဗီုကဵု sulfonamides ကဵု antiseptics) လေဝ် နွံကီုရ။ ဆဂး နဲကဲသီုၜါပြကာဂှ် ရန်တၟအ် သွက်ဂွံ ဂစိုတ် သတ်မဳခရဝ် ဟွံသေင်မ္ဂး စဵုဒၞာညံင် သတ်မဳခရဝ် ဟွံဂွံ ဗြေဝ်တိတ်ရ။ တုဲပၠန် သီုၜါဂှ် နွံဒၟံင် ကုဂြန်ဓါတုအာန္တိမဳခရဝ်ဗိ ရ။ ကိရိယာအာန္တိဗက်တေရဳယာဂမၠိုင် မပ္တံကဵု ဂဥုဲအာန္တိသေပ်တိစ်ဂမၠိုင် (antiseptic drugs)၊ အာန္တိဗက်တေရဳယျာသောပ် (ဗံင် ဂစိုတ်စၟ) (antibacterial soaps)၊ ကေုာံ ကပေါတ်ဓါတု သမ္အးဇမ္ၚးဂမၠိုင် (chemical disinfectants)တအ်ဂှ် စုတ်လဝ် ဂြန်ဓါတုအာန္တိဗိသြတိစ်ဖအိုတ်ရ။[၅] လဆောဝ်မ္ဂး ပ္ဍဲကဵု စၞစအဓိကဂမၠိုင်လေဝ် စုတ်လဝ် ဂွံဆဵုကေတ်ကီုရ။
နိရုတ်
[ပလေဝ်ဒါန် | ပလေဝ်ဒါန် တမ်ကၞက်]ဝေါဟာရမ္ဂး အာန္တိဗိသြသိသ် 'antibiosis', မဂွံအဓိပ္ပါယ် "ဒစဵုဒစးလမျီု"၊ ဂှ် မၞိဟ်မစကာ ကိုပ်ကၠာအိုတ် အစာဗက်တေရဳယျာဗေဒ ဂကူပြင်သေတ် ဂျေန် ပေါလ် ဝူလေမိန် (Jean Paul Vuillemin) မချူဗၟံက် ဂဥုဲဂစိုတ်ဗက်တေရဳယျာ ကိုပ်ကၠာအိုတ်ဂှ်ရ။[၆][၇]
ဝေါဟာရ အာန္တိဗိသြတိစ် antibiotic ဂှ် စကာကၠာအိုတ် ပ္ဍဲသၞာံ ၁၉၄၂ နကဵု သေလ်မာန် ဝက်သၟာန် Selman Waksman ပ္ဍဲကဵု လိက်ပရေင်ညး မချူလဝ် ပရူဗီုလွဳပ္တိတ် သဝ်မဳခရဝ် ဂှ်ရ။[၆] အခိင်လၟုဟ် ဝေါဟာရမ္ဂး အာန္တိဗိသြတိစ်ဂှ် ရန်တၟအ်ကဵု အရေဝ်အဓိပ္ပါယ် မဂစိုတ် ဟွံသေင်မ္ဂး မထိင်ဒဝ်လဝ် ဗက်တေရဳယျာတုဲ ဂဥုဲမကၠောန်ပ္တိတ်လဝ် နကဵု သတ်မဳခရဝ် ကဵုဒှ် နကဵုဓါတုကဵုဒှ် ကော်စ အာန္တိဗိသြတိစ် ဖအိုတ်ရ။[၈][၉]
ဝေါဟာရ အာန္တိဗိသြတိစ် "antibiotic" ဂှ် ကၠုင်နူ anti + βιωτικός (biōtikos), "ဒစဵုဒစး လမျီု",[၁၀] မဒှ် ဝေါဟာရ မကၠုင်နူ βίωσις (biōsis), "ဒတန်လမျီု/ဘဝ",[၁၁] မကၠုင် နူ βίος (bios), "လမျီု/ဘဝ"။[၁၂] ဝေါဟာရ အာန္တိဗက်တေရဳယျာ "antibacterial" ဂှ် ကၠုင်နူ ဂရိတ် ἀντί (အာန္တိ anti), "ဒစဵုဒစး"[၁၃] + βακτήριον (baktērion ဗက်တေရိအောန်)၊ မကၠုင် နူ βακτηρία (baktēria ဗက်တေရိယာ), "ၜဝ်",[၁၄] ဟိုတ်နူ ဗက်တေရဳယျာဂှ် ဂွံဆဵုကေတ် ကၠာအိုတ် နူကဵု လေအ်ၜဝ်။
ပဋိဇဳဝ ဂှ် ဒှ်မအရေဝ် ပါဠိ ပဋိ (ဒစဵုဒစး) မတုပ်ကဵု အာန္တိ၊ ဇဳဝ ဂှ် လမျီု။ မအရေဝ်ဝွံ ၜိုန်ရ နကဵု လိက်စကာဒၟံင်ကီုလေဝ် ပ္ဍဲကဵု လဟီု ကေုာံ စကာကွေဟ်ကွေဟ်ဂှ် အောန်ဗွဲမလောန်တုဲ စၞးဂှ် ဟီုဂးဒၟံင် အာန္တိဗိသြတိစ် ဂၠိုင်ရ။
လွပ်
[ပလေဝ်ဒါန် | ပလေဝ်ဒါန် တမ်ကၞက်]ဂဥုဲ
[ပလေဝ်ဒါန် | ပလေဝ်ဒါန် တမ်ကၞက်]အာန္တိဗိသြတိစ်ဂှ် စကာကၠုင် သွက်ဂွံလွဳ ဟွံသေင်မ္ဂး စဵုဒၞာ သရ/ယဲဂမၠိုင် မကတဵုဒှ် ဟိုတ်နူဗက်တေရဳယျာ၊[၁၅] လဆောဝ်မ္ဂး ယဲမကတဵုဒှ် ဟိုတ်နူ ပရဝ်တဝ်ဇြဝ်လေဝ် လွဳဒၟံင်ကီုရ။ (မေတြဝ်နိဒဇြဝ်လေ (Metronidazole) ဂှ် နွံကဵု အာနိသံသ မဒစဵုဒစး ကုယဲမကတဵုဒှ် ဟိုတ်နူ ပရသိတ် (ပရုန်))။ အခိင်ကာလ မဒှ်သံသယျ ယဲမွဲ က္တဵုဒှ် ဟိုတ်နူ ဗက်တေရဳယျာ၊ ဆဂး ဗက်တေရဳယျာလဵုမွဲ မဒှ်မာန်ဂှ် ဟွံဂွံတီဏီမ္ဂး ဒးစကာ နဲကဲအစမ်အၜတ် (empiric therapy) ဒးစမ်ပါ်ယဲ သွက်ဂွံတီ ဟိုတ်ယဲ။ အရာဏအ်ဂှ် ဒးကေတ်အခိင် တ္ၚဲဗွဲမဂၠိုင်မာန်ရ။
အခိင်ကာလ ဟိုတ်ယဲမဂွံကတဵုဒှ်ဂှ် တီလဝ်တုဲတုဲမ္ဂး စလွဳနဲကဲမတီယဲ (definitive therapy) ဂွံရ။ ကာလဂှ်မ္ဂး စကာ ဂဥုဲအာန္တိဗိသြတိစ် မဆေင်စပ် ကုယဲဂှ်မာန်ရ။ can be started. This will usually involve the use of a narrow-spectrum antibiotic. The choice of antibiotic given will also be based on its cost. Identification is critically important as it can reduce the cost and toxicity of the antibiotic therapy and also reduce the possibility of the emergence of antimicrobial resistance.[၁၆] To avoid surgery, antibiotics may be given for non-complicated acute appendicitis.[၁၇]
Antibiotics may be given as a preventive measure and this is usually limited to at-risk populations such as those with a weakened immune system (particularly in HIV cases to prevent pneumonia), those taking immunosuppressive drugs, cancer patients, and those having surgery.[၁၅] Their use in surgical procedures is to help prevent infection of incisions. They have an important role in dental antibiotic prophylaxis where their use may prevent bacteremia and consequent infective endocarditis. Antibiotics are also used to prevent infection in cases of neutropenia particularly cancer-related.[၁၈][၁၉]
The use of antibiotics for secondary prevention of coronary heart disease is not supported by current scientific evidence, and may actually increase cardiovascular mortality, all-cause mortality and the occurrence of stroke.[၂၀]
ဂၠံင်တရဴ မလွဳ
[ပလေဝ်ဒါန် | ပလေဝ်ဒါန် တမ်ကၞက်]ဂၠံင်တရဴမလွဳ နကဵု အာန္တိဗိသြတိစ်ဂှ် နွံနာနာသာ်ရ။ ဗွဲမဂၠိုင်မ္ဂး စကာနကဵု မဖျုင်ပၠုပ် ဂၠံင်ပါင်ဂၠိုင်ရ။ လဆောဝ်မ္ဂး မထပက်ပၠုပ် နကဵုတၞုင်လေဝ် နွံကီုရ။[၁][၁၆] ဂဥုဲအာန္တိဗိသြတိစ်ဂှ် ကၠောန်လဝ် နကဵု ထၞဟ်မန်၊ ထၞဟ်ကတောဝ်တအ်လေဝ် နွံကီုရ။ နကဵု ဂဥုဲလံက် ပ္ဍဲစၞာံလေဝ် ဂွံဆဵုကေတ် ဗွဲမဂၠိုင်ကီုရ။[၂၁] ဂလိုင်မသုင်ဂှ်လေဝ် တန်တဴဒၟံင် သရ/ယဲ ကေုာံ ဇမၞော်ဇကု မၞိဟ်မယဲဂှ်ရ။ တုဲပၠန် ယဲဂှ်သာစှ်ေမ္ဂး ဒးသုင်ဖအောန်ဖျေဟ် နကဵုသၞောတ်စှ်ေစှ်ေ၊ သုင်ဂၠိုင်ၜက်လေဝ် ဒှ်အောန်အန္တရာယ်၊ အောန်အာလေဝ် ဗက်တေရဳယျာ ဂွံအာ ဒြဟတ်ဒုင်ပဒဝ် ဂဥုဲတုဲ လွဳယဲဟွံဗၠး ဒှ်မာန်ကီုရ။[၂၂] ပ္ဍဲကာလ မဒးလွဳယဲဗီုကဵု ကရေက်မ္ဂး စကာ အာန္တိဗိသြတိစ် ညံင်ဒၞာဲကရေက်လဝ် ဟွံဂွံဒှ်သရ။[၂၃]
လွပ်
[ပလေဝ်ဒါန် | ပလေဝ်ဒါန် တမ်ကၞက်]ဍုင်မွဲကုမွဲ ဂလိုင် မစကာ အာန္တိဗိသြတိစ် ဟွံတုပ် ရေင်သကအ်ရ။ ဂကောံထတ်ယုက်ဂၠးကဝ် (WHO) ပ္တိတ် လိက်ဒုင်စဳရေင် သၞာံ ၂၀၁၈ မဒုင်သဇိုင် ကုတင်ဂၞင် နူသၞာံ ၂၀၁၅ နူကဵု ၆၅ ဍုင်။ ပ္ဍဲမၞိဟ် ၁,၀၀၀ ဂှ် စကာ မွဲသွုင် ပ္ဍဲမွဲတ္ၚဲ။ ရးနိဂီုမောန်ဂဝ်လဳယျာဂှ် စကာဂၠိုင်အိုတ် နွံကဆံင် ၆၄,၄ တုဲ ဍုင်မစကာ အောန်အိုတ်ဂှ် ဒှ်ဍုင် ဗူရုန်ဒဳ နကဵု ၄,၄ ရ။ ပၞောဝ်ကဵု ဂဥုဲဂမၠိုင်ဂှ် Amoxicillin ကဵု amoxicillin/clavulanic acid ဂှ် ဒှ်ဂဥုဲ မစကာဂၠိုင်အိုတ်ရ။[၂၄]
နိဿံသဂမၠိုင် (side effects)
[ပလေဝ်ဒါန် | ပလေဝ်ဒါန် တမ်ကၞက်]
အာန္တိဗိသြတိစ်ဂှ် စမ်ၜတ်လဝ် နာနာသာ် ညံင်ဟွံဂွံဒှ် အန္တရာယ် ကုညးမစကာ နူကိုပ်ကၠာ ဟွံစကာ နဒဒှ်ဂဥုဲဏီတုဲ ဗွဲမဂၠိုင်မ္ဂး နွံကဵုဂီုကၠီု တုဲ တေအ်ဒၟံင်ရ။ ဆဂး အာန္တိဗိသြတိစ်လ္ၚဵုဂှ် မလေပ် ကဵုနိဿံသ ညိည စဵုကဵု ဗွဲမသကာတ်မြဟ်မာန်တုဲ ညးမွဲကုညးမွဲလေဝ် ဟွံတုပ် ရေင်သကအ်ရ။ ညးလ္ၚဵုဂှ် ဟွံတေအ် ကုအာန္တိဗိသြတိစ် နွံမာန်ရ။[၂၅]
နိဿံသ လပါ်ပရေအ်ဂမၠိုင်ဂှ် ယဝ်ရ မသုင်ကေတ်လဝ်မ္ဂး မလေပ်ဒှ်မာန် ဗီုကဵု ဂၞဴလီု။[၂၆] ညံင်ဟွံဂွံဒှ်ဗီုဂှ် သုင်ကဵု ဂဥုဲ ပရဝ်ဗိသြတိစ် (probiotics) မ္ဂး စဵုဒၞာကဵု ညံင်ဂၞဴဟွံဂွံလီုမာန်ကီုရ။[၂၇] အာန္တိဗိသြတိစ်ဂှ် သီုကဵု ခဍဳလျတ်ဒး vaginal flora မာန်ကီုတုဲ ဍေဟ်မပကဵု ညံင် yeast ဂွံဂၠိုင်တိုန် ဗွဲတၟေင် ပ္ဍဲဒၞာဲယောနိမၞိဟ်ဗြဴတအ်ရ။ နိဿံသဏအ်လေဝ် ဗဒှ်ဖအောန်ဖျေဟ် နကဵု ဂဥုဲတၞဟ်မာန်ကီုရ။[၂၈]
အာန္တိဗိသြတိစ် လ္ၚဵုဂှ် ပလီုကဵု မိတဝ်ခေါန်ဒြိယန် (mitochondrion)၊ မဒှ်အရာမကၠောန်ပ္တိတ် ဗိတေရဳယျာ မနွံ ပ္ဍဲ eukaryotic, သီုကဵု ကလာပ်ရုပ်တၞဟ်တအ်ကီုရ။[နွံပၟိက် ဗၟံက်ထ္ၜးတင်နိဿဲ] ဟိုတ် မိတဝ်ခေါန်ဒြိယန် ဂွံလီုဂှ် ဟိုတ်နူကဵု ကလိုက်ကမဵု အံက်ဇြဳဒေန် (oxidative stress) ပ္ဍဲကလာပ်ရုပ်ဂမၠိုင်၊ ကေုာံ ပရေင်ခဍဳလျတ် နူကဵု fluoroquinolones မြဴသာ်ဝွံ ပတှ်ေကေတ်လဝ်ရ။[၂၉] ဍေဟ်တအ် သီုကဵုမကော်စ ခဍဳလျတ် ခလဝ်ရဝ်ပလေတ် (affect chloroplasts)။[၃၀]
ကသဳမွဲဟာန်ဂမၠိုင် (Interactions)
[ပလေဝ်ဒါန် | ပလေဝ်ဒါန် တမ်ကၞက်]ဂဥုဲ စဵုဒၞာ ကောန်
[ပလေဝ်ဒါန် | ပလေဝ်ဒါန် တမ်ကၞက်]အရာလဵု အာန္တိဗိသြတိစ် မဟွံဂွံကိတ်ဂှ် လ္ၚတ်တုဲ ဂွံဆဵုလဝ် နွံကီုရ။[၃၁] ဗွဲမဂၠိုင် ဂွံဆဵုကေတ် ဂဥုဲ စဵုဒၞာ ကောန်ဂှ် ကသဳမွဲဟာန် (သုင်မွဲစွံ) ဟွံဂွံ။ သုင်ဒးမ္ဂး ဗီုကဵု ဂၞဴအာ၊ ဂအအ်တအ် ကတဵုဒှ်မာန်ရ။[၃၁]
အလ်ကဝ်ဟဝ် (အရက်)
[ပလေဝ်ဒါန် | ပလေဝ်ဒါန် တမ်ကၞက်]ကသဳမွဲဟာန် (သုင်မွဲစွံ) ကုအလ်ကဝ်ဟဝ် (အရက်)မ္ဂး နိဿံသ ပရေအ်ပရေအ်ဂမၠိုင် က္တဵုဒှ်မာန် တုဲပၠန် အာန္တိဗိသြတိစ်လေဝ် ဍေဟ်ဟွံကၠောန် ကမၠောန်ကီုရ။ အာန္တိဗိသြတိစ် ဓမ္မတာဂှ်မ္ဂး သုင်မွဲစွံ ကုအရက်ဟွံဂွံဂှ်ဂၠိုင်၊ ဆဂး တန်တဴဒၟံင် ဂကူအာန္တိဗိသြတိစ်တုဲ ဂဥုဲလ္ၚဵုဂှ် ဟွံကဵုအန္တရာယ်လေဝ် နွံကီုရ။[၃၂]
ဗဒုင်ဗဒဝ် (Resistance)
[ပလေဝ်ဒါန် | ပလေဝ်ဒါန် တမ်ကၞက်]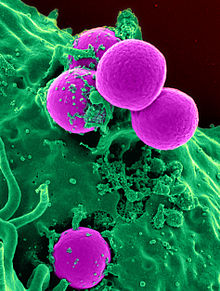
ဗက်တေရဳယျာ မဒုင်ဗဒဝ် အာန္တိဗိသြတိစ် (antibiotic-resistant bacteria) ဂှ် ဒှ်အရာဓမ္မတာမွဲ မကတဵုဒှ်ဒၟံင်ရ။ ဟိုတ်ဍေဟ် မကတဵုဒှ်ကၠုင် ဗီုဏအ်ဂှ် ဟိုတ်နူမစကာ အာန္တိဗိသြတိစ်တုဲ နကဵုလၟေင်ကသုဲသဘာဝ (evolutionary processes) ဂှ် သွက်ဂွံဒုင်ဒဝ် အာန္တိဗိသြတိစ်ဂှ် ဗက်တေရဳယျာတအ် ဖန်ဇန် ပလေဝ်စဇကုတုဲ ဗဳဇတၟိ မဒုင်ဗဒဝ် အာန္တိဗိသြတိစ် က္တဵုဒှ်ကၠုင်ရ။ ဂဥုဲအာန္တိဗိသြတိစ် မစကာဂၠိုင် ဗီုကဵု ပေန်နဳသဳလိန် (penicillin) ကဵု ဨရဳထြဝ်မဳသိန် (erythromycin) တအ်ဂှ် ဟိုတ်နူ မဂစိုတ် ကဵုဂကူဗက်တေရဳယျာ ဗွဲမဂၠိုင်မာန်တုဲ စကာဂၠိုင်အိုတ်ရ။ ဟိုတ်နူ မစကာဂၠိုင်တုဲ ဗက်တေရဳယျာတအ် ကၠောန်ဗဒှ်ဗဳဇတၟိတုဲ လၟုဟ် ဂစိုတ်ကဵု ဗက်တေရဳယျာမာန် အောန်အိုတ်၊ မြဴသာ်ဝွံ ဒှ်ကၠုင်ရ။
ဝင်
[ပလေဝ်ဒါန် | ပလေဝ်ဒါန် တမ်ကၞက်]ကိုပ်ကၠာ ၂၀ ဗွဝ်ကၠံ လပါ်စဂှ် ယဲသရဂမၠိုင်ဂှ် လွဳကၠုင် နကဵုဂဥုဲဒဗျဂမၠိုင်ရ။ ဂဥုဲဒဗျ ဗစိန်သရဂှ် ကောန်မၞိဟ်တအ် လွဳကၠုင် နူကဵုသၞာံ ၂,၀၀၀ ပြင်င်တေအ်ရ။[၃၃]
အာန္တိဗိသြတိစ် မစကာ ပ္ဍဲဂဥုဲ ခေတ်တၟိဏအ်ဂှ် စကတဵုဒှ်ကၠုင် ကြဴနူ မဂွံဆဵုကေတ် အာန္တိဗိသြတိစ် မဂွံနူ အသာ်ဂမၠိုင်ရ။[၃၄][၃၅]

ဒဒှ်မလွဳယဲ နကဵုဂဥုဲဓါတ် အာန္တိဗိသြတိစ် နကဵုနဲသိပ္ပံ ကိုပ်ကၠာအိုတ်ဂှ် ကၠုင်နူ ရးနိဂီုဂျာမနဳ နကဵု ပေါလ် အေရ်လိချ် (Paul Ehrlich) ပ္ဍဲကၞောတ် ၁၈၈၀တအ်ရ။ နကဵုလညာတ် အေရ်လိချ်မ္ဂး ဍာ်ဂဥုဲအသာ်တအ်ဂှ် ဖျောန်ကဵု ကလာပ်ရုပ် မၞိဟ်၊ တိရစ္ဆာန် ကေုာံ ဗက်တေရဳယျာတအ်မာန်ရ။ နူဂှ် မွဲကဆံင် ညးကလိဂွံ ကသပ်မွဲ ဒုင်သဇိုင် ကုသဘာဝဂှ်တုဲ ကၠောန်ပ္တိတ် ဓါတ် မဂစိုတ် ဗက်တေရဳယျာမာန် သီုကဵု ဟွံကဵုဘဲအန္တရာယ် ကုမၞိဟ်တအ် ဂွံမာန်ရောင်ရ။ ကြဴနူ ညးလ္ၚတ် အသာ်ဂမၠိုင် နူကဵု သဘာဝနာနာတုဲ ပ္ဍဲသၞာံ ၁၉၀၇ ဂှ် ညးကၠောန်ပ္တိတ် ဂဥုဲဂစိုတ်ဗက်တေရဳယျာ လၟုဟ်ကော်စ arsphenamine ရ။

ပေနဳသဳလ်လိန် (Penicillin) ကဵု အာန္တိဗိသြတိစ် သဘာဝဂမၠိုင်
[ပလေဝ်ဒါန် | ပလေဝ်ဒါန် တမ်ကၞက်]
နိဿဲ
[ပလေဝ်ဒါန် | ပလေဝ်ဒါန် တမ်ကၞက်]- ↑ ၁.၀ ၁.၁ Antibiotics. NHS (5 June 2014).
- ↑ Factsheet for experts. European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Archived from the original on 2014-12-21။ Retrieved on 2022-08-31။
- ↑ (2012) Chemical Analysis of Antibiotic Residues in Food.. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.။
- ↑ Why antibiotics can't be used to treat your cold or flu (2017-05-06).
- ↑ General Background: Antibiotic Agents. Alliance for the Prudent Use of Antibiotics.
- ↑ ၆.၀ ၆.၁ (2015) "Chapter 8: Microbes in Production of Fine Chemicals (Antibiotics, Drugs, Vitamins, and Amino Acids)", Applied Microbiology. Springer India, 83–120. doi:10.1007/978-81-322-2259-0. ISBN 978-81-322-2258-3။
- ↑ "Early descriptions of antibiosis" : 889–94.
- ↑ (2000) The Antimicrobial Drugs. Oxford University Press, US, 3. ISBN 978-0-19-512529-0။
- ↑ "Origins and evolution of antibiotic resistance" : 417–33. doi:.
- ↑ "βιωτικός", A Greek-English Lexicon။
- ↑ "βίωσις", A Greek-English Lexicon။
- ↑ "βίος", A Greek-English Lexicon။
- ↑ "ἀντί", A Greek-English Lexicon။
- ↑ "βακτηρία", A Greek-English Lexicon။
- ↑ ၁၅.၀ ၁၅.၁ (2011) Antibiotics Simplified.. Jones & Bartlett Publishers, 15–17. ISBN 978-1-4496-1459-1။
- ↑ ၁၆.၀ ၁၆.၁ "General principles of antimicrobial therapy" (February 2011). Mayo Clinic Proceedings 86 (2): 156–67. doi:. PMID 21282489.
- ↑ "Antibiotics Versus Appendicectomy for the Treatment of Uncomplicated Acute Appendicitis: An Updated Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials" (October 2016). World Journal of Surgery 40 (10): 2305–18. doi:. PMID 27199000.
- ↑ "Antimicrobial prophylaxis and outpatient management of fever and neutropenia in adults treated for malignancy: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline" (February 2013): 794–810.
- ↑ "Infection in neutropenic patients with cancer" (July 2013): 411–41.
- ↑ "Antibiotics for secondary prevention of coronary heart disease" (February 2021). The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2 (5): CD003610. doi:. PMID 33704780.
- ↑ "Topical antibiotic treatment for uncomplicated skin and skin structure infections: review of the literature" (October 2009).
- ↑ "Topical antimicrobial therapy for treating chronic wounds" (November 2009).
- ↑ "Topical antibiotics for preventing surgical site infection in wounds healing by primary intention" (November 2016).
- ↑ "UK antibiotic consumption twice that of the Netherlands, WHO report finds"၊ Pharmaceutical Journal၊ 14 November 2018။ 31 August 2022 တင်နိဿဲဏအ် စၟဳစၟတ်တုဲ။ Archived from the original on 22 December 2018။
- ↑ "A clinician's guide to the appropriate and accurate use of antibiotics: the Council for Appropriate and Rational Antibiotic Therapy (CARAT) criteria" (July 2005).
- ↑ Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea – All you should know.
- ↑ "PURLs: prescribing an antibiotic? Pair it with probiotics" (March 2013).
- ↑ "Fluoroquinolones and tendinopathy: a guide for athletes and sports clinicians and a systematic review of the literature" (1 January 2014).
- ↑ "{{{title}}}" (March 2018).
- ↑ "{{{title}}}" (October 2015).
- ↑ ၃၁.၀ ၃၁.၁ "Antibiotics and OC effectiveness" (January 2013). JAAPA 26 (1): 11. doi:. PMID 23355994.
- ↑ "Risks of combined alcohol/medication use in older adults" (March 2007). The American Journal of Geriatric Pharmacotherapy 5 (1): 64–74. doi:. PMID 17608249.
- ↑ "Take Two Beers and Call Me in 1,600 Years: Use of Tetracycline by Nubians and Ancient Egyptians" (2000). Natural History (5; May): 50–53.[permanent dead link]
- ↑ "The introduction of 'chemotherapy' using arsphenamine - the first magic bullet" .
- ↑ (1941) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. New York: Macmillan။
- All articles with dead external links
- Articles with dead external links from November 2023
- Articles with invalid date parameter in template
- Articles with permanently dead external links
- Pages using ISBN magic links
- Pages using PMID magic links
- All articles with unsourced statements
- Articles with unsourced statements from January 2022
- ဂဥုဲ
- သိပ္ပံ
